Bull Pine Tree Information
Images of Bull Pine:


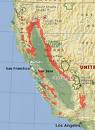



Bull Pine grows in the following 1 states and provinces:
CaliforniaInformation about Bull Pine:
The Pinus Sabiniana is commonly known as the Bull Pine, Foothills Pine as well as Gray Pine.
The currently accepted scientific name for gray pine is Pinus sabiniana Dougl. . There are no recognized subspecies, varieties, or forms .Gray pine is endemic to California. It is distributed from Siskiyou County south through the foothills of the Klamath, Cascade, and Coast ranges and the Sierra Nevada to Ventura County . Near its southernmost Sierra Nevada limit, gray pine is absent from a 55-mile (89-km) stretch between Kings River and the South Fork of the Tule River .Gray pine and blue oak (Quercus douglasii) occur together over much of California's oak woodlands. The blue oak-gray pine community varies in stand density and composition, often sharing dominance with several other tree species. The understory may be mostly grasses, shrubs, or mixtures of both . Pure stands of gray pine occur in localized areas of serpentine soil , but more often, blue oak provides more cover within the community type. At lower elevations, the blue oak-gray pine woodland grades into chaparral, valley oak (Q. lobata) woodland, or Oregon white oak (Q. garryana) woodland. At higher elevations, it mixes with California black oak (Q. kelloggii) or ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) forest . In its easternmost distribution, gray pine merges with desert communities such as western juniper (Juniperus occidentalis) and big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) near the Great Basin and singleleaf pinyon (P. monophylla)-California juniper (J. californica) near the Mojave Desert . Plant associates: Overstory associates not mentioned in Habitat Types and Plant Communities or SAF Cover Types include Coulter pine (P. coulteri), California buckeye (Aesculus californica), interior live oak (Quercus wislizenii), bigcone Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga macrocarpa), and MacNab cypress (Cupressus macnabiana) . Common shrub associates include toyon (Heteromeles arbutifolia), wedgeleaf ceanothus (Ceanothus cuneatus), chamise (Adenostoma fasciculatum), California scrub oak (Q. dumosa), desert scrub oak (Q. turbinella), California buckthorn (Rhamnus californicus), common manzanita (Arctostaphylos manzanita), birchleaf mountain-mahogany (Cercocarpus betuloides), poison-oak (Toxicodendron diversilobum), Sargent cypress (Cupressus sargentii), and hollyleaf cherry (Prunus ilicifolia) . Common ground associates include slender oat (Avena barbata), California buckwheat (Erigonum fasciculatum), soft chess (Bruomus hordeaceus), ripgut brome (B. rigidus), cutleaf filaree (Erodium cicutarium), bur clover (Medicago hispida), ground lupine (Lupinus bicolor), and tarweed (Hemizonia spp.) . Publications listing gray pine as a dominant or codominant species are as follows: A classification system for California's hardwood rangelands Blue oak communities in California Association types in the North Coast Ranges of California Natural terrestrial communities of California Some of the information provided here is attributed to:Howard, Janet L. 1992. Pinus sabiniana. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). , available at the USDA Fire Effects Information System (FEIS) website